
The vestibule connects the cochlea to the labyrinth, a set of semicircular canals that control balance. This membrane is called the basilar membrane because it serves as the base, or ground floor, on which key hearing structures sit. An elastic membrane runs from the beginning to the end of the cochlea, splitting it into an upper and lower part. EAR CANAL The ear canal starts at the outer ear and ends at the ear drum. There are three different parts to the outer ear the tragus, helix and the lobule. The outer ear is made up of cartilage and skin.

The medical term for the outer ear is the auricle or pinna. The cochlea, also known as the organ of hearing, is shaped much like a snail’s shell and has small hair cells called cilia that are bathed in fluid. This structure helps to give each of us our unique appearance. The final part of the ear is called the inner ear, which includes the cochlea, the vestibule, and the labyrinth. In both ears, the Eustachian tube serves as a pressure-equalizing valve and drains any fluid that collects in the middle ear into the back of the throat. The air chamber in the middle ear connects to the back of the nose via the Eustachian tube. Normal hearing occurs when the sound waves pass through the ear canal and vibrate the ear drum. They connect the ear drum to the inner ear and are named the malleus, or hammer, incus, or anvil, and stapes, or stirrup. The middle ear is an air-filled chamber containing three small bones called ossicles. The ear drum, or tympanic membrane, is a thin membrane that separates the outer ear from the middle ear.
HAMMER ANVIL EAR SKIN
The outer ear consists of skin and cartilage, called the auricle, or pinna, and the ear canal. Each part has an important function in the hearing process. It’s divided into three parts called the outer, middle, and inner ear. The ear is made of flexible, soft tissue that attaches to the side of the head. Wispr University Hammer, Anvil & Stirrup by otoscopy. DoD-VA Hearing Prosthetics Ordering System.Hearing Evaluation & Treatment Solutions.

These cells turn sound vibrations into electrical signals that are sent to the brain. When the stapes bone moves, fluid in the inner ear moves and stimulates hair cells in the inner ear. Standards and Clinical Practice Guidelines The ear drum sends these vibrations to the small bones in the middle ear: the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil), and stapes (stirrup).HCE Collaborative Auditory / Vestibular Research Network (CAVRN).
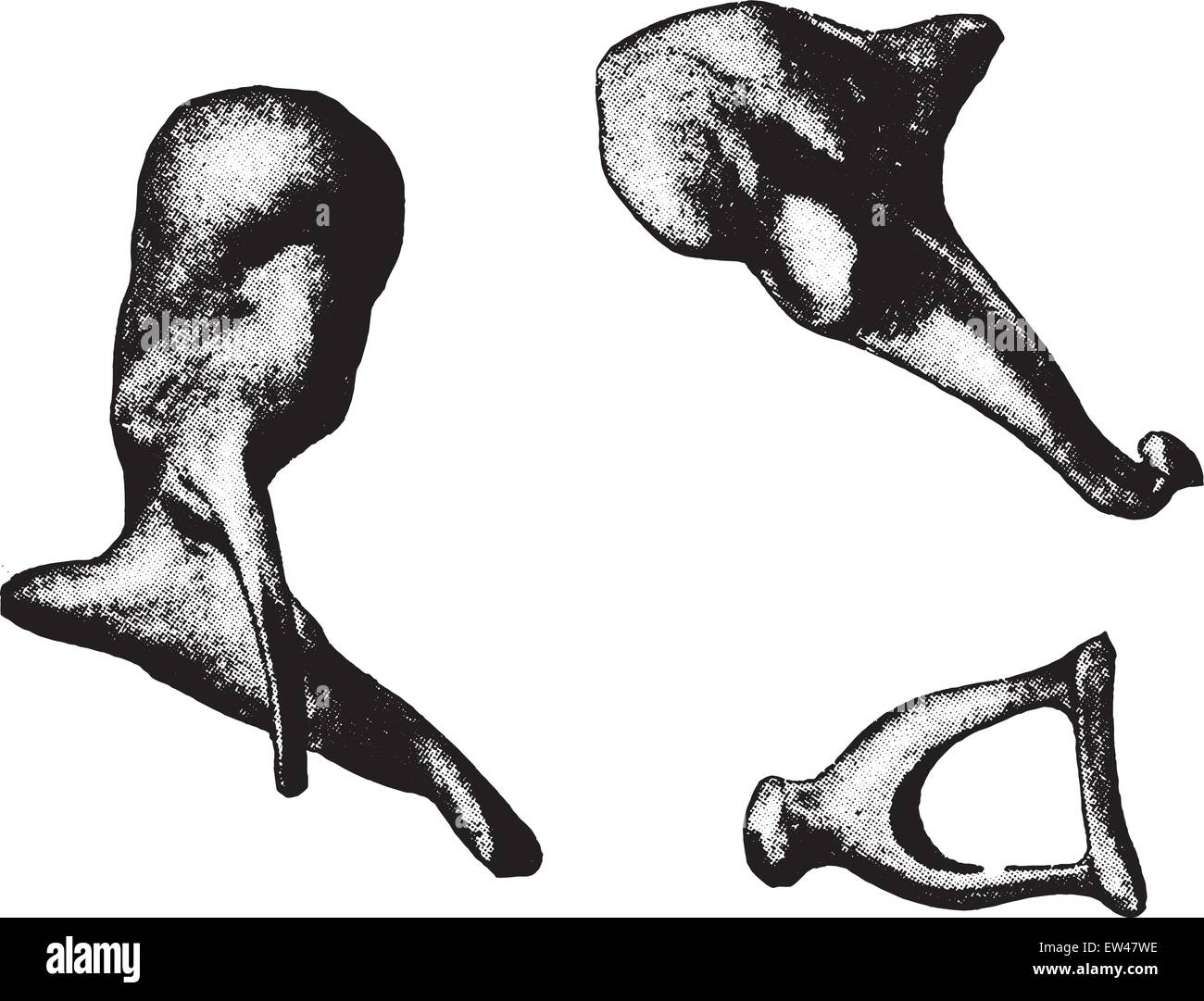
MRI can thus be considered safe in usual clinical settings, as far as our studied implants are concerned. The displacement of three of the prostheses in water is not relevant in real clinical situations. The implanted piston in the temporal bone did not move. However, while in the water-filled Petri dish, three of these moved with the flux. None of the prostheses was displaced in the empty Petri dish. In situ testing was done by implanting a piston in a cadaveric temporal bone and performing MR sequences any possible displacement was then assessed by CT scan and under microscopic vision. Eventual in vitro displacement was assessed visually by two means. Most of the prostheses were then placed in a water-filled Petri dish and reintroduced into the MRI unit. Nine middle ear prostheses (seven containing stainless steel and two made of pure gold used as control) were tested in vitro and one stainless steel stapedectomy prosthesis was tested on a cadaveric temporal bone.Įach metallic prosthesis was placed in an empty Petri dish and introduced into a 1.5-tesla (T) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) unit. Investigation of the effects of magnetic resonance fields on commonly used metallic middle ear implants.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
